“`html
Effective Ways to Find Slope in 2025: Practical Tips and Techniques to Master!
Understanding the Slope Formula
The **slope formula** is a fundamental concept in mathematics that helps us ascertain the **slope of a line**. It represents the ratio of the vertical change (rise) to the horizontal change (run) between any two points on a line. The formula itself is expressed as slope (m) = (change in y) / (change in x) or more explicitly as m = (y2 – y1) / (x2 – x1). This equation allows us to easily calculate the slope when provided with the coordinates of two points. Knowing how to apply this equation is crucial for understanding various applications such as graphing linear equations and analyzing real-life data where changes occur.
The Meaning Behind Slope
Slope has various definitions in mathematics, physics, and real-life applications, making it an important concept to grasp. The **slope** characterizes the steepness or inclination of a line or surface. A **positive slope** indicates that as one variable increases, the other variable does too, whereas a **negative slope** suggests an inverse relationship where an increase in one results in a decrease in another. Understanding the **slope meaning** in different contexts, such as in coordinate geometry or physics, shows how slope can indicate trends and rates of change across various datasets. For instance, in business, a rise over run could represent the cost in relation to quantity produced.
The Importance of Calculating Slope
Calculating the **slope** is essential not only in theoretical mathematics but also in practical scenarios, such as data analysis and engineering designs. The **slope measurement** can help determine trends in data sets, making it easier to interpret results from graphs. It also plays a significant role in calculus, where the **instantaneous slope**, often found using derivatives, helps in understanding the behavior of functions at specific points. Whether you’re working on slope calculations for residential construction or analyzing financial trends, mastering the **slope techniques** is key to effective problem-solving.
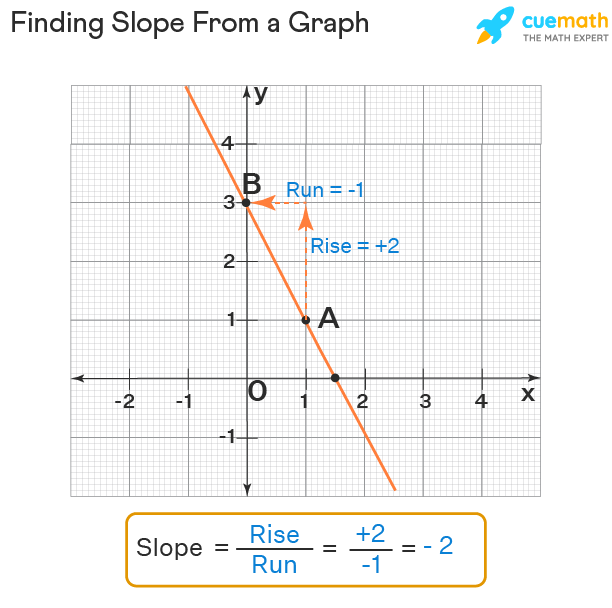
Slope in Graphs: Visual Representation
Visualizing the **slope of a line** on a graph can greatly enhance understanding. Graphically, a line’s **slope** can be represented with the help of the **slope triangle**, which shows the rise and the run. A quick way to estimate slope is to draw these triangles right on the graph and measure the respective sides. For instance, in a line represented in a graph, if it rises 3 units vertically and runs 4 units horizontally, the slope is calculated as 3/4. This visual technique helps in perceiving not just the slope size but also its direction—upwards for positive slopes and downwards for negative slopes, thus assisting in sectors like engineering where precise slopes are crucial.
Common Slope Graph Types
There are several common types of **slope graphs** you may encounter: linear, steep, gentle, horizontal, and vertical. Each type portrays various interactions between variables. For example, a **horizontal slope** (slope of 0) indicates no change in the y-value regardless of changes in the x-value, often visualizing a steady state or equilibrium in economic models. Conversely, a **vertical slope** (undefined slope) reflects an instant change, suitable for curves that have steep inclines. Knowing the type of slope helps in understanding the functionalities of graphs in various disciplines, be it in mathematics or the social sciences.
Applying Slope in Real Life
The practical applications of **slope** extend beyond academia; it has considerable implications in the real world. For instance, in construction, the **slope significance** can be noticed in drainage systems where not having an adequate slope can lead to water accumulation problems. In physics, slope supports the analysis of velocity on distance-time graphs, helping students grasp rates of change effectively. Additionally, analyzing slope in statistics helps in understanding correlations between variables, thus enhancing decision-making processes in fields such as economics and marketing.
Effective Techniques for Slope Calculation
Employing effective techniques to **find slope** can significantly ease the learning curve for students and professionals alike. One fundamental method involves using the **slope intercept form** of a linear equation given by y = mx + b, where m represents the slope. This is particularly useful for plotting graphs from equations and understanding their characteristics based on their slopes.
Practical Examples of Finding Slope
A common example of calculating slope involves determining the slope between two points. For instance, if we have two points A(2, 3) and B(5, 7), the slope (m) can be determined as:
m = (y2 – y1) / (x2 – x1) = (7 – 3) / (5 – 2) = 4/3.
This practical example not only teaches the concept of slope but also reinforces graphing skills by identifying the coordinates accurately.
Engaging with Slope Problems
To master slope-related concepts, engaging with various **slope problems** and practice sets is invaluable. Solving problems involving both positive and negative slopes, analyzing zero slopes, and understanding slope implications in different contexts helps refine one’s ability to calculate slopes efficiently. Familiarity through repeated practice strengthens one’s capacity to **determine slope** and apply this mathematical understanding in real-life scenarios or advanced subjects like calculus and statistics.
Conclusion
Mastering the concept of **slope** encompasses understanding its formula, significance, and applications in various fields, as well as developing calculation techniques that make finding slope easier. The interplay of these techniques promises not only improvements in mathematical capacity but also enhances its practical usage across several domains. With the insights provided in this article, you’re set to move forward confidently in your pursuit of understanding and applying slope effectively.
Key Takeaways
- The slope formula relates vertical and horizontal changes.
- Slope has a variety of applications in both academic and real-world contexts.
- Visualization using slope graphs and triangles can aid understanding.
- Consistent practice with slope problems is crucial for proficiency.
- Real-world applications of slope demonstrate its broad significance.
FAQ
1. How do I calculate the slope between two points?
To calculate the slope between two points, use the slope formula:
m = (y2 – y1) / (x2 – x1). By substituting the y-coordinates and x-coordinates of the points into this formula, you can easily determine the slope. For example, if you have points (1, 2) and (4, 8), plug them into the formula: m = (8 – 2) / (4 – 1) = 6/3 = 2. Thus, the slope in this case is 2.
2. What is the slope of a horizontal line?
The slope of a horizontal line is always zero. This means there is no vertical change as you move along the line; thus, the vertical rise (change in y) is 0, making the slope (0/run) = 0, regardless of the run, which can be any non-zero value.
3. What does a negative slope indicate?
A **negative slope** indicates that as one variable increases, the other variable decreases. For instance, a line going downwards from left to right signifies a negative slope. This can be particularly important in financial contexts where rising costs correspond with declining profits. Understanding the implications of negative slopes can help tackle challenges in business and economics efficiently.
4. Can slope be undefined?
Yes, slope can be undefined, which typically occurs with vertical lines. In such cases, the change in x is 0, and thus, the slope formula leads to division by zero, resulting in an undefined slope. This is crucial for recognizing the characteristics of linear functions.
5. How does slope apply in calculus?
In calculus, the slope represents the rate of change of a function at any given point and is calculated using derivatives. Finding the slope of a function’s tangent line at a specific point can provide insights into its behavior, such as identifying local maxima and minima. Understanding slope in the context of calculus enhances skills needed for analyzing complex mathematical functions.
“`