“`html
How to Find the Area of a Shape: A Practical Guide for 2025
Understanding how to find the area of a shape is essential for countless applications in daily life, from DIY home projects to advanced engineering calculations. Areas provide vital information when measuring spaces and determining material quantities. This guide offers a straightforward approach to calculating area, with specific formulas and examples tailored for various shapes including squares, rectangles, circles, and triangles.
Key Concepts in Area Measurement
To effectively measure area, we first need to grasp basic principles and terms. **Area** is defined as the amount of space inside a two-dimensional shape. It’s measured in square units, indicating how many unit squares can fit into the shape. Understanding geometry area calculations is fundamental, whether you’re working with the area of simple shapes or irregular forms. Here we will cover basic concepts and some practical tips that flatten the learning curve on how to calculate area.
Basic Area Concepts and Formulas
The area formula is essential for any geometric shape. For **squares**, the area is calculated by squaring the length of one side (area = side^2). The area of rectangles can be found using the formula area = length × width. When it comes to triangles, the formula simplifies to area = 1/2 × base × height. Circles introduce a new variable, as area = π × radius². These formulas represent fundamental steps in finding area and should be memorized for swift reference.
Using Online Calculators for Area Measurement
In today’s tech-driven era, leveraging **online calculators for area** can simplify our calculations immensely. Websites and apps can handle conversion between different units, providing instant area results without needing extensive calculations. Specifically designed tools for calculating the area of various shapes can make the process not only faster but also allows for exploring complex designs and determining area in real-world applications, such as landscape design or architectural projects.
Real-World Applications of Area
Areas play a significant role in various sectors. In construction, accurately calculating the area is essential for resource management. Similarly, in landscaping and architecture, knowing the **area of irregular shapes** aids in planning and design considerations. This practical approach also extends into physics, where understanding surface areas is pivotal in applications like fluid dynamics or thermal dynamics, demonstrating the real-life significance of mastering area calculations.
Calculating Area of Specific Shapes
Now that we have covered basic area principles, let’s dive deeper into calculating the area for specific geometric shapes. Knowing **how to measure area** for different forms will enhance problem-solving skills and enable functionality across diverse applications, from academia to everyday situations.
Finding Area Using Length and Width
Calculating the area of rectangles and parallelograms primarily revolves around using their length and width. For rectangles, simply multiply the two dimensions (area = length × width). Parallelograms, while appearing less straightforward, use a similar methodology by taking height into account—the formula being area = base × height. Understanding how to apply these formulas helps identify dimensions effectively leading to accurate findings.
Area of Circles and Ellipses
Circles and ellipses present unique challenges within geometry. As mentioned, the area of a circle relies on the simple formula A = π × radius². When considering ellipses, calculating area utilizes the semi-major and semi-minor axes (area = π × semi-major × semi-minor). Utilizing precise measurements will yield accurate area determinations—a vital aspect whether for academic purposes or project execution.
Exceptional Cases: Trapezoids and Irregular Shapes
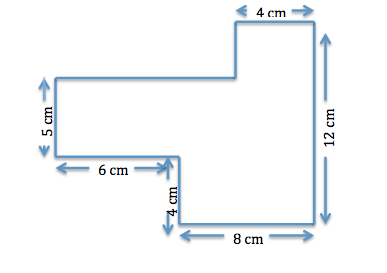
Calculating the area of trapezoids can prove slightly more complex. The formula, area = 1/2 × (base1 + base2) × height, requires a firm understanding of its measurements. Furthermore, the area of irregular shapes can be determined using grid estimation or the **unit square area** method, aligning a shape over a grid and counting the squares covered. Techniques such as decomposing irregular shapes into simpler geometric forms can streamline the calculation process.
Challenges and Solutions in Area Calculation
Calculating area can present various challenges, particularly for those less acquainted with geometry. Utilizing straightforward hints and tools can simplify understanding and bolster confidence, ensuring effective and accurate measurements.
Addressing Area Problems with Solutions
One common area problem occurs when varying the units of measurement, requiring **area conversion formulas**. For instance, converting square meters to square feet may necessitate specific mathematical conversions. Practical area problems often pop up in environmental studies or land and agriculture, where precise shapes need accurate area evaluations for effective resource allocation.
Exploring Area Concepts Through Teaching and Learning
Engaging in practical exercises, such as quizzes, can foster a deeper understanding of area concepts. Resources that focus on **teaching area concepts**, particularly for younger students or high school curricula, can enhance comprehension. Tools such as area measurement apps can provide interactive lessons tailored for learners of varying levels.
Visualizing Area for Enhanced Comprehension
Utilizing diagrams and illustrations is crucial when learning how to find the area. Visual area lessons can clarify complex shapes and provide tangible examples of how area plays out in real-world scenarios. This **visualization of area** can make concepts more tangible, improving overall understanding and introduction to advanced area applications.
Key Takeaways
- Understanding *how to find the area of a shape* is essential for various applications.
- Mastering basic area formulas enhances problem-solving efficiency.
- Online tools simplify calculations and conversion tasks for area measurement.
- Visual learning aids solidify comprehension and practical application of area concepts.
FAQ
1. What is the significance of unit square area in area measurements?
Unit square area refers to the measure of area derived from single unit squares. It serves as the basis for calculating larger areas and emphasizes the spatial properties of two-dimensional shapes. Understanding unit square areas can aid in visualizing and contextualizing the space shapes occupy.
2. How can I calculate area for mixed units?
For mixed units, start by converting them into a consistent measurement. Find a reliable *area conversion formula*, switch all lengths into, say, feet or meters before calculating. This approach ensures accurate area readings regardless of the initial unit discrepancies.
3. Can online tools really help with calculating irregular areas?
Absolutely! Many online calculators offer options for irregular shapes, enabling precise area calculations with user-friendly interfaces. These tools can greatly enhance methodological approaches to identifying irregular areas and facilitate accurate measures based on individual inputs.
4. What methods can be used to simplify complex area problems?
Breaking down complex shapes into simpler components can simplify area problems considerably. Techniques such as drawing auxiliary lines to create measurable segments and applying established area formulas streamline the process, making area calculations more manageable.
5. How is area related to principles in physics and engineering?
Area features prominently in both physics and engineering concepts, particularly in areas concerning forces, pressure, and fluid dynamics. Understanding the properties and mathematical implications of area can inform material usage, design considerations, and spatial arrangements within these disciplines.
“`