Effective Ways to Learn How to Find IQR
Understanding IQR and Its Importance
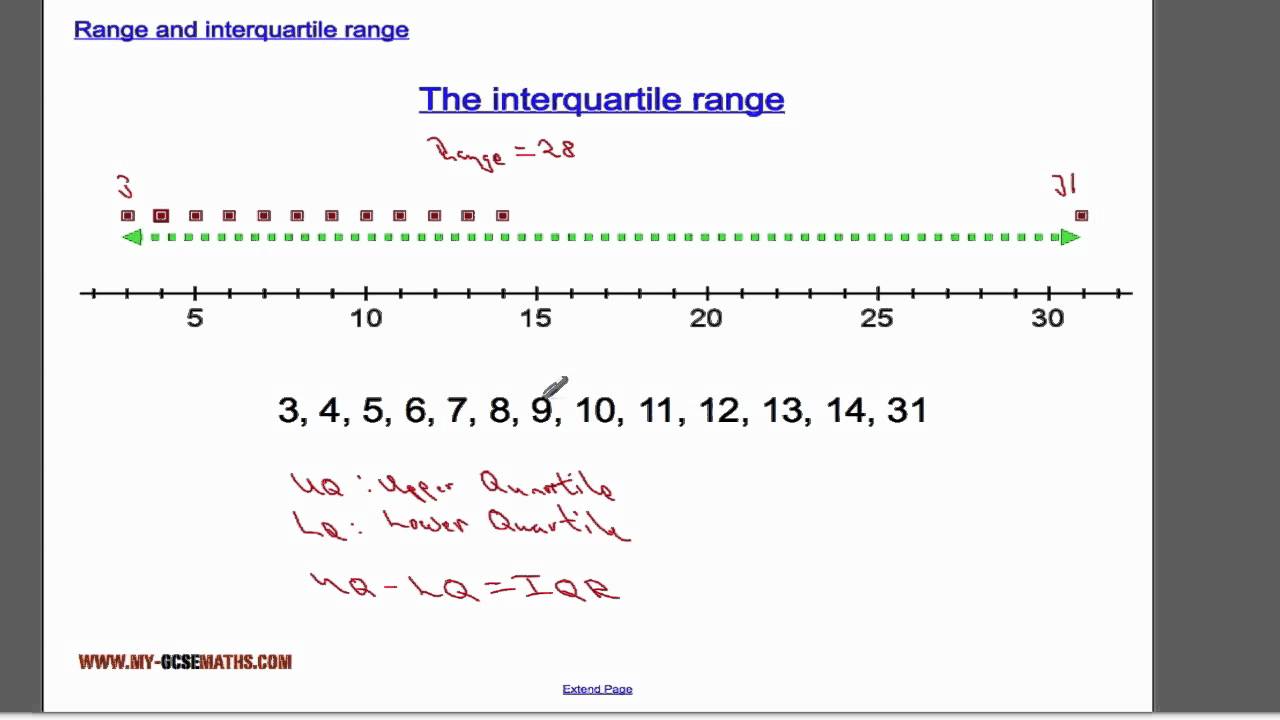
The **Interquartile Range (IQR)** is a fundamental concept in statistics that measures the statistical dispersion within a data set. It represents the range between the first (lower) and third (upper) quartiles. By determining how to **find IQR**, you can better understand the variability and spread of your data. Investigating the **quartiles and IQR** specifically allows analysts to minimize the influence of outliers and better interpret central tendencies in their data. The significance of the **IQR formula**, which subtracts the lower quartile from the upper quartile, provides a clear method to calculate **IQR** and assess the data distribution comprehensively.
What is IQR?
The **IQR definition** encompasses the differences between the first and third quartiles—essentially, it captures the middle 50% of data points in a dataset. It is essential for understanding data consistency, as it excludes outliers which can skew the data’s true spread. This metric is particularly useful in exploratory data analysis (EDA), providing quick insights by summarizing the central cluster of values without letting extreme values shift analyses profoundly. Familiarity with the **statistical methods** related to IQR can significantly enhance your skill set in data analysis.
Why is IQR Significant?
The **importance of IQR** lies in its ability to reveal potential outliers within a dataset. When analyzing data, knowing how to **calculate IQR** helps establish boundaries beyond which values can be considered outliers. In the realm of descriptive statistics, analyzing variability helps practitioners to evaluate the consistency of the data representations effectively. A good grasp of measures like the IQR contributes to better decision-making in diverse fields such as healthcare, finance, and social sciences, emphasizing its critical role in **data analysis**.
Steps to Calculate IQR
To effectively **calculate IQR**, it’s crucial to follow systematic **IQR calculation steps**. By adhering to these steps, you’ll streamline your data processing, ensuring accurate results every time. Let’s utilize an example to illustrate these steps clearly.
Finding Quartiles
The first step in determining the IQR involves **finding quartiles**. Start by arranging your dataset in ascending order. Once the data is sorted, the **lower quartile (Q1)**, which is the median of the first half of the data, and the **upper quartile (Q3)**, the median of the second half of the data, can then be identified. This process aids in a clearer understanding of the data distribution and allows analysts to uncover essential trends existing between these quartiles. This straightforward approach helps in performing thorough **data analysis**, providing the groundwork for reliable outcomes.
Calculating IQR Example
Using a practical example makes the IQR clearer. Suppose the dataset is: {3, 7, 8, 12, 14, 18, 20}. First, find **Q1** and **Q3**. Arrange the data and identify the middle point (the median), which divides the dataset into two halves. The lower quartile is 7, while the upper quartile is 18. Therefore, the **IQR calculation** will involve subtracting these quartiles: IQR = Q3 – Q1 = 18 – 7 = 11. This calculated numerical data aids in visualizing the dataset’s spread, confirming that there are no extreme values within the middle range of this dataset.
IQR in Box Plots and Outlier Detection
The **IQR in box plots** is mostly implemented to graphically summarize data points and outliers. Box and whisker plots employ the IQR as a foundation for recognizing extreme values visually. The rectangular box represents the **quartile range**, while lines, known as “whiskers,” extend to demonstrate variability outside this range. Understanding the connection between IQR and box plots is vital in statistics, allowing for effective visual representation of data spread and assisting in assessing the overall **data distribution analysis**.
Identifying Outliers
Outlier detection is crucial in statistical data modeling. With outliers potentially skewing averages and leading to misinterpretation in your analysis, knowing how **IQR significance** plays into outlier function is paramount. Typically, any data point lying beyond 1.5 times the **IQR** from Q1 or Q3 will be flagged as an outlier. This numerical construct aids in tightening data interpretations. For example, consider lower bounds as Q1 – 1.5 * IQR and upper bounds as Q3 + 1.5 * IQR to establish limits encompassing typical dataset values.
Box Plot Interpretation
A well-constructed box plot reveals extensive insights about any data set and makes interpretation straightforward. The **data representation** shared through this graphical illustration highlights the IQR while enabling a quick sight of both central tendency and data spread. For practitioners, interpreting of **box plot values** offers a fundamental grasp of the data set and its characteristics, particularly valuable for pinpointing areas that require deeper investigation or correction.
Applications of IQR in Data Analysis
The applications of **IQR for data distribution** cut across various domains from business to health sciences. For statisticians and data analysts alike, understanding the power that comes from utilizing IQR assists in creating actionable insights that drive data-driven decisions. This makes the IQR an invaluable tool in any analyst’s toolkit, particularly for summarizing large datasets.
Applications in Business
In business analytics, employing **IQR** aids in qualitative decisions that impact strategic planning. With the extraordinary amount of data that flows through companies, having an effective way to assess changes in performance is invaluable. Using IQR helps to analyze sales trends, compare sector performances, and provide robust insights necessary for informed decision-making. Businesses can forecast potential sales fluctuations and prepare strategic responses ahead of time.
IQR in Machine Learning
In the realm of machine learning, IQR plays a critical role in **data preprocessing** and feature selection. By revealing the spread of data and pinpointed instances of **outliers**, data scientists utilize IQR to enhance model accuracy. For accurate training of predictive models, removing outlier data points mitigates bias, enhancing the overall integrity of machine learning algorithms. This importance of IQR in balancing datasets leads to improved predictions and stability in model performance.
Key Takeaways
- The IQR helps to measure variability while guarding against outlier biases.
- Understanding how to find IQR enhances data interpretation and representation skills.
- Calculating IQR is fundamental in statistical analyses and can be incorporated to improve predictive analytics.
- Box plots utilize IQR, visualizing data spread and highlighting potential outliers effectively.
FAQ
1. What is the basic IQR formula?
The **IQR formula** is relatively simple: IQR = Q3 – Q1, where Q3 is the upper quartile and Q1 is the lower quartile. This difference provides a measure of the spread of the middle 50% of the data points, highlighting data consistency.
2. How do quartiles relate to IQR?
Quartiles provide the foundation for calculating the IQR. The first quartile (Q1) marks the cutoff for the lowest 25% of data points, while the third quartile (Q3) indicates the cutoff for the highest 25%. The difference between these values forms the IQR, indicating the central dispersion in the data.
3. Why should one use IQR instead of standard deviation?
The choice between using **IQR** and standard deviation depends on data characteristics. The IQR is less affected by outliers than standard deviation. Therefore, if the dataset contains extreme values, the IQR provides a more reliable volumetric analysis of data spread.
4. How can IQR help in outlier detection?
IQR aids in outlier detection by establishing bounds: values more than 1.5 times the IQR from Q1 or Q3 are considered outliers. This statistical mechanism ensures that analyses focus on significant data points devoid of extreme values.
5. How is IQR used in exploratory data analysis?
In exploratory data analysis, IQR aids in visualizing data shapes and identifying variability quickly. Analysts use box plots combined with IQR to compare distributions across datasets efficiently, making it an invaluable tool in any analyst’s repertoire.