How to Calculate Percent Error for Accurate Results in 2025
Understanding **how to calculate percent error** is essential for obtaining accurate results in various fields such as science, engineering, and data analysis. Percent error provides insight into the precision and reliability of measurements. In this article, we will explore comprehensive methods for **calculating percent error**, its significance across different domains, and practical examples to enhance your understanding.
Defining Percent Error
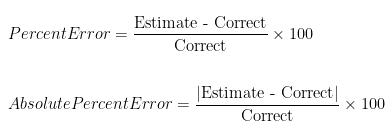
Before diving into the calculations, it’s crucial to have a clear **percent error definition**. Percent error is a measure that expresses the difference between the measured value and the true value as a percentage of the true value. This metric is invaluable in many disciplines, including experimental science, engineering, and research. The basic **percent error formula** is:
Percent Error = (|Measured Value – True Value| / |True Value|) × 100%
Using this formula, one can easily assess the accuracy of their results. The absolute difference between the measured and true values provides insight into the extent of error, making it easier to evaluate performance, especially in experimental setups.
Understanding the Percent Error Calculation
When **calculating percent error**, the first step is to ensure you have accurate values. This involves precise measuring techniques and an understanding of **measurement uncertainty**. Let’s consider an example: If a scientist measures the boiling point of water in a controlled environment as 98.5°C, while it’s known to be 100°C at sea level, we can calculate the percent error as follows:
1. Calculate the absolute error: |98.5 – 100| = 1.5
2. Apply it to the formula: (1.5 / 100) × 100% = 1.5%
This example highlights how to find percent error effectively, demonstrating a clear and straightforward method for assessing measurement reliability in practical uses such as **percent error in experiments**.
Common Applications of Percent Error in Science
In scientific contexts, interpreting **percent error in physics** and chemistry often reveals discrepancies between expected and actual outcomes. Accurate **percent error calculations in labs** provide critical insights into the validity of experimental results. For instance, when evaluating the yield of a chemical reaction, noticing a significant **percent error** could prompt a reevaluation of procedures and materials to improve accuracy. Familiarity with techniques like **determining percent error** can vastly improve experimental integrity and outcomes.
Importance of Percent Error in Data Collection
Applying **percent error in data collection** involves quantifying uncertainties to improve data accuracy in statics and research methodologies. Assessing error is vital to achieving valid conclusions in experimental and real-world scenarios. Without understanding **error analysis**, you may misinterpret results, leading to incorrect conclusions.
Percentage Error and Measurement Precision
When dealing with measurement activities, understanding measurement uncertainty and **statistical percent error** becomes critical. For example, researchers could use marginalization techniques to analyze how varying measurements impact overall data integrity. The importance of reporting extremely low or high **percent error** highlights potential issues in measurements and allows for corrections to enhance the validity of claims made:
1. Enhance the reliability of experimental conclusions;
2. Fine-tune results based on measured discrepancies.
This form of **percent error analysis** lays out a roadmap to mitigate errors, thus enhancing the assertion of scientific reliability.
Tips for Avoiding Percent Error
A key component to achieving accurate results is recognizing potential sources of error. **Avoiding percent error** requires meticulous planning and execution in the measurement phase. Here are a few practical strategies to reduce errors:
- Calibrate instruments before use to ensure accuracy;
- Use multiple trials to average out anomalies;
- Incorporate control groups wherever applicable;
- Spend extra time in recognizing **significant figures** and data precision.
Implementing these techniques can markedly enhance the overall accuracy of percent error calculations.
Common Mistakes in Percent Error Calculations
Even experienced professionals can make mistakes in **calculating percent error**. One frequent pitfall involves confusion between **percent error** and **absolute error**. For example, while absolute error quantifies the magnitude of the difference between two measured values, percent error expresses this difference relative to the true value.
Calculating Errors in Practical Scenarios
To solidify your understanding, let’s tackle a practical example directly from a laboratory environment. A chemistry experiment concludes with the determination of 95 grams of product expected to yield. The actual yield observed is only 80 grams. To compute pacific values, ensure the accurate substitution into the handy percent error formula:
Percent Error = (|80 – 95| / |95|) × 100% = (15 / 95) × 100% ≈ 15.79%
This elucidates not merely a number but serves as a foundational analysis of the entire experiment’s reliability.
Significance of Percent Error in Educational Settings
The teaching of **percent error** in classrooms is instrumental to developing analytical skills in students. Classroom activities geared at exploring various experiments offer real-time insight into error analysis. By exploring the **percent error method**, educators can create an engaging learning environment that enhances comprehension of scientific principles:
For instance, implementing virtual labs can shine attention on how **calculating percent error** is executed in experimental setups significantly, allowing for improved data collection practices and results discussions.
Key Takeaways
1. Understanding and computing **percent error** can significantly enhance data and measurement accuracy in various fields.
2. Utilizing proper formulas, forensic practices in measurement, and error evaluation can minimize relaying significant errors in experimental contexts.
3. Frequent, collaborative experiments help in statistically gauging precision and understanding the importance of ensuring accurate methodologies.
FAQ
1. What is the most common use of percent error?
The most common application of **percent error** is in scientific experiments, where it measures the accuracy of experimental results compared to accepted or known values, essential for validating scientific hypotheses, and ensuring consistency across data sets.
2. How do you differentiate between percent error and percent change?
**Percent error** quantifies the difference between a measured value and a true value, whereas **percent change** highlights the increase or decrease between two numbers. Understanding this distinction is crucial in accurately reporting data and its implications.
3. Can percent error ever be negative?
No, **percent error** is expressed as a positive figure since it reflects the magnitude of error rather than its directional influence. Always use absolute values in the calculation to maintain the non-negativity.
4. Why is percent error significant in engineering?
In engineering, **percent error** is vital for ensuring designs meet safety and performance benchmarks. By quantitatively assessing discrepancies, engineers can refine their designs while consistently enhancing the reliability of their projects.
5. How to report percent error in scientific papers?
When citing **percent error** in scientific papers, express it alongside the results under analysis. Properly state the original and measured values used in calculations to provide context for the reported data, thereby enhancing the transparency and credibility of your research.