How to Properly Calculate Density: A Guide for Students in 2025
Understanding and calculating density is essential for students in various fields, including science and engineering. This guide aims to clarify density calculations and provide practical steps to ensure accurate results. By mastering density calculations, students can strengthen their foundational knowledge and apply it effectively in real-life scenarios.
Understanding Density Calculation
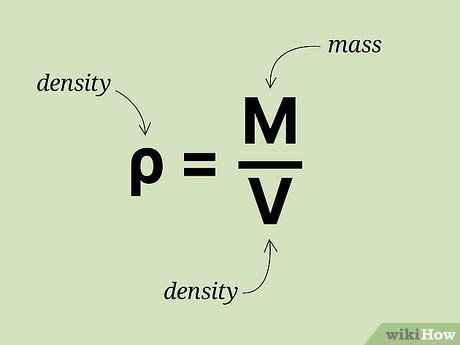
Density is defined as the mass of an object divided by its volume. The formula to calculate density is straightforward and can be summarized as follows:
Density (ρ) = Mass (m) / Volume (V)
The units of density are typically expressed in grams per cubic centimeter (g/cm³) or kilograms per cubic meter (kg/m³). For example, if a substance has a mass of 200 grams and occupies a volume of 50 cubic centimeters, the calculation would be:
Density = 200 g / 50 cm³ = 4 g/cm³
By applying this fundamental concept, students can explore various applications of density. It is crucial to ensure accurate measurement of mass and volume to find the correct density. Further, you can experiment with different materials to see how their density varies, enhancing your understanding of the relationship between mass and volume.
Measuring Mass Correctly
To accurately measure the mass of an object, using a balance or scale is essential. Here are some practical steps to ensure accurate measurement:
- Choose the Right Balance: Select a scale appropriate for the weight of the object you are measuring, ensuring it has suitable precision.
- Zeroing the Balance: Before placing the object on the scale, ensure that the balance reads zero (tare) to eliminate excess weight.
- Take Multiple Measurements: Measure the mass multiple times to account for variations and average them for accuracy.
By mastering these techniques, you can ensure that the mass you record is precise, allowing for correct density calculations in your experiments.
Accurate Volume Measurement Methods
Once you have the mass, the next step is to measure the volume accurately. The method you choose will depend on the physical state of the substance:
- Liquid Volume: Use a graduated cylinder or pipette for precise measurement. Make sure to read the meniscus at eye level to avoid parallax errors.
- Solid Volume: Calculate the volume of regular solids using mathematical formulas or employ water displacement for irregular objects. To use water displacement, record the water level in a graduated cylinder, submerge the object, and measure the new water level.
Using these volume measurement techniques helps you ensure that your final density calculations are based on accurate data.
Application of Density in Real Life
Understanding density has practical implications in various fields, from science and engineering to everyday life. For instance, in buoyancy studies, objects less dense than the fluid they’re in will float, while denser objects will sink. This principle is fundamental in designing boats and ships, where understanding the density of materials is crucial for buoyancy and stability.
Density in Materials Science
In materials science, density plays a vital role in determining material properties. Different materials have unique density values that can affect their strength, durability, and overall utility. For example, metals like lead have a high density and are used in applications requiring durability, while lightweight materials like aluminum are preferred in aerospace engineering due to their low density.
Students exploring engineering or design fields can benefit from understanding how to select materials based on density requirements, optimizing the performance of their projects.
Buoyancy and Density in Engineering
Engineering applications frequently involve calculating the density of materials to design elements with desired buoyant properties. When designing a vessel, engineers must ensure that the overall density is less than that of the water it displaces, thus allowing for buoyancy. This involves considerations of both the materials used and the structure’s overall design to achieve the right balance of density and functionality.
Understanding these principles allows future engineers to create more efficient and effective designs across various sectors, including marine and aerospace industries.
Common Mistakes in Density Calculation
Despite its simplicity, students often make several common mistakes when calculating density. Identifying these errors can greatly improve accuracy in density calculations.
Incorrect Measurement Techniques
One common mistake is using inaccurate measurement techniques. As previously discussed, precision is crucial in both mass and volume measurement. Always ensure that you are using calibrated equipment and appropriate techniques for the material type. For liquids, avoid bubbles in graduated cylinders, while for solids, ensure they are clean and dry before measuring.
Students should regularly verify measurement methods to develop consistency in their density calculations.
Misunderstanding Density Concepts
Another mistake involves misunderstandings of the density concept itself. Students may confuse weight with mass, or volume with density, leading to incorrect calculations. It’s crucial to grasp that weight is the force exerted by gravity on an object while density relates to mass and volume.
Using dimensional analysis can often help clarify these concepts. For example, always remember that mass is in grams or kilograms, volume in cubic centimeters or meters, which will help reinforce the units associated with density.
Summary and Key Takeaways
In this guide, we have explored the fundamental principles of density calculation:
- The definition and formula for density.
- Accurate methods for measuring mass and volume.
- Practical applications and implications in real-life scenarios like engineering and materials science.
- Common mistakes and misconceptions to avoid.
By following the outlined strategies and refining your approach, you’ll enhance your skills in calculating and applying density effectively in various contexts.
FAQ
1. How do I find the density of an object if I know its mass and volume?
To find the density, use the formula Density = Mass / Volume. Simply divide the mass by the volume to obtain the density value, ensuring you use consistent units such as grams for mass and cubic centimeters for volume.
2. Can density change with temperature?
Yes, density can change with temperature. As most substances are heated, they expand, thereby increasing volume and reducing density. Conversely, as substances cool, they contract, generally resulting in a higher density.
3. What units are commonly used for density measurements?
Common units for density include grams per cubic centimeter (g/cm³) for solids and liquids, and kilograms per cubic meter (kg/m³) widely used in scientific contexts. Selecting appropriate units is essential for clear communication of measurements.
4. How does the density of water compare to that of other substances?
The density of water is 1 g/cm³ at 4°C. Substances with a density less than this will float, while those with a higher density will sink. This property of water makes it an essential reference point in density studies.
5. What role does density play in buoyancy?
Density is the key factor determining buoyancy; objects less dense than the fluid they are submerged in will float, while those more dense will sink. This principle is crucial in designing floating objects like boats and ships.
6. Where can I learn more about calculating density?
For additional resources on calculating density and related topics, check out this link: How to Calculate Density.
7. Are there any tools available for measuring density?
Yes, there are various tools for measuring density, including hydrometers for liquids, digital balances for mass measurement, and graduated cylinders or measuring cubes for volume. Each tool serves a specific purpose in achieving accurate density calculations.