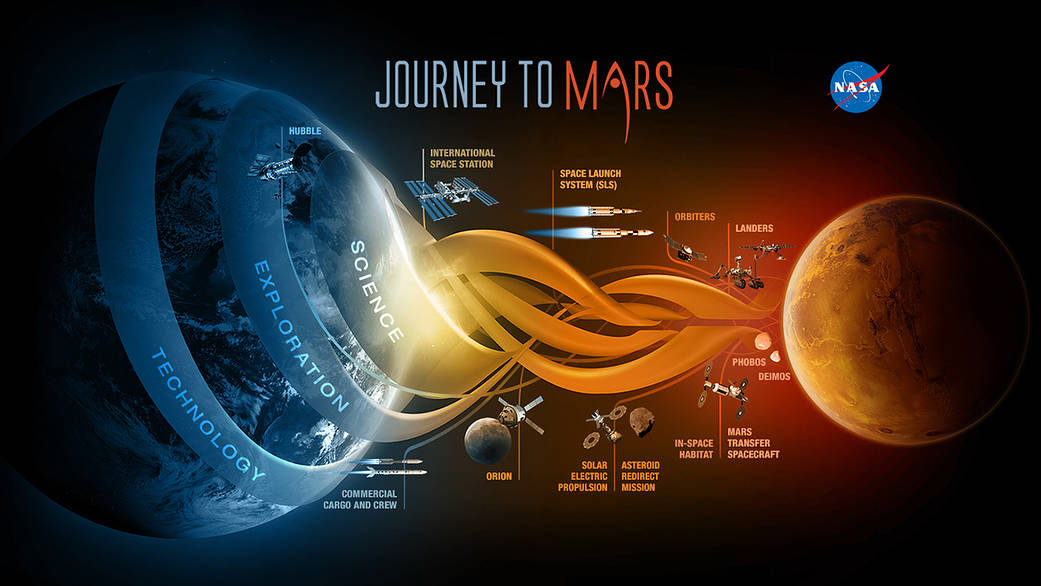
Effective Ways to Get to Mars: Understanding the Timeline in 2025
The concept of **traveling to Mars** has tantalized humanity for decades. With increasing discussions around feasible missions, understanding the **travel time to Mars** becomes essential for planning future **interplanetary travel**. This article focuses on the time estimates, phases of **getting to Mars**, and the various considerations that come into play during a **Mars journey**. Facts and projected missions will provide insights into this remarkable undertaking, particularly how long we anticipate space travelers will take to reach the Red Planet by 2025.
Understanding Mars Journey Time
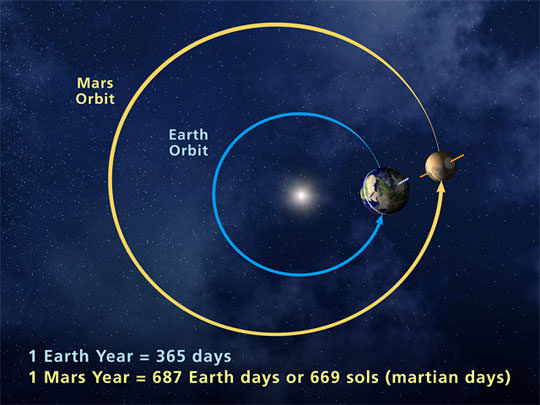
The **Mars journey time** significantly depends on various factors, including spacecraft velocity, launch windows, and the planetary alignment between Earth and Mars. Typically, the **Mars travel duration** can vary from six to nine months, but this estimation can change based on orbital positions. Utilizing time calculations for space travel, scientists can predict the best **travel durations for different spacecraft** and plan launch dates meticulously.
Calculating Travel Time to Mars
To calculate the **time needed to get to Mars**, we primarily rely on the distance between the two planets, which varies significantly over their orbits. The shortest distance occurs approximately every 26 months during a phenomenon called opposition. Using this as a benchmark, spacecraft engines must provide a consistent thrust to maintain optimal speed throughout their journey. For instance, NASA’s Perseverance rover was launched during such a favorable period, with its **trip length to Mars** clocking in at about 7 months, illustrating how critical such calculations are in the planning stages.
Phases of a Human Trip to Mars
A **human trip to Mars** is divided into distinct phases: launch, interplanetary transit, entry, descent, and landing. During the launch phase, powerful rockets propel the spacecraft away from Earth’s gravitational pull. Following this, the **Mars mission duration** becomes heavily influenced by the spacecraft’s speed. Developing new engines that maximize fuel efficiency, like ion propulsion, could drastically reduce the **Mars travel estimates** and enhance the chances of human colonization. Each of these phases presents challenges and time considerations that must be accounted for.
Understanding Mars Orbital Travel Time
Another consideration for **Mars orbital travel time** involves the spacecraft’s trajectory. This intricate calculation is essential for ensuring that the spacecraft arrives at Mars when the planet is optimally positioned for landing. Using advanced **trajectory calculations for Mars**, mission planners can pinpoint the best windows to embark on a successful Mars mission. Moreover, real-time data about the **Mars surface conditions** is examined to ensure both the safety and efficiency of the entire **journey phases to Mars**.
Challenges of Flying to Mars
Flying to Mars isn’t just about overcoming distances; it involves facing numerous challenges as well. From the **Mars terrain challenges** to environmental conditions, each element affects the **Mars expedition duration** significantly. As missions are planned, understanding how these variables play into overall travel timelines will determine the success of such ambitious endeavors.
Impact of Mars Gravity on Travel
The **effects of Mars gravity on travel** are notable, as they can impact everything from landing protocols to human health. With roughly 38% of Earth’s gravity, astronauts will experience different conditions upon arrival. The **Mars gravity effects on travel** can influence the design of spacesuits and habitats built for sustainable **living conditions on Mars**. Awareness of these factors shapes both preparation and the anticipated duration of the mission.
Experiencing Space Radiation During Mars Travel
Space radiation is another challenge that cannot be overlooked. During a typical **Mars journey duration**, astronauts will be exposed to heightened levels of cosmic radiation, posing health risks. Ensuring the spacecraft provides adequate shielding against radiation will extend the timeline of a mission forecast and prepare astronauts for safe **living sustainably on Mars**. Research on spacecraft materials and crew training will need to address this challenge to minimize its impact on **Mars travel duration**.
Preparing for the Psychological Effects of Mars Travel
Long missions such as those needed for **flying to Mars** can contribute to psychological stress among crew members, leading to behavioral issues that can hinder mission success. It’s crucial to establish strategies for mental well-being, thereby ensuring astronauts can engage in team-building exercises while in transit. Anticipating and planning for the **psychological effects of Mars travel** can greatly improve the morale and productivity of the crew throughout the mission.
Future Mars Missions and Exploration Plans
The timeline for **future Mars missions** continues to evolve, with both governmental and private entities actively exploring the Red Planet’s potential. Understanding the **Mars exploration missions** not only emphasizes technological advancements but fuels public interest in space tourism and colonization. Various **NASA Mars plans** include robotic explorations that will pave the way for human presence on Mars, fundamentally changing how we think about space travel.
The Role of Robots in Mars Exploration
Robots serve as pioneers on Mars, sending back invaluable data about the **Mars surface** and environment. Instruments aboard these robots collect information that helps to evaluate the safety and viability for human safety. With **the role of robots in Mars exploration** funneling data into future mission planning, they contribute substantially to refining timelines and understanding what humans will face upon arrival.
Tourism Potential on Mars
As technology improves and safety measures evolve, the idea of **Mars tourism potential** becomes more tangible. Future missions will likely pave the way for advanced **Mars transport systems** compatible with human travel. Understanding the recreational aspects of Mars will necessitate clear calculations about **interplanetary travel to Mars**, including estimates of travel fees, experiences, and timelines for tourists eager to explore the extraterrestrial landscape.
Spacecraft Innovations for Mars Travel
As we progress toward launching human missions, examining **spacecraft types for Mars travel** is pivotal. Innovations in design and engineering can improve efficiencies and decrease mission costs as well as time spent in transit. New technologies such as nuclear thermal propulsion are being explored for their potential to cut down on **time needed to get to Mars** drastically. Innovations of this nature will impact how humans design their interactions with both spacecraft and Martian environments.
Key Takeaways
- The **travel time to Mars** typically ranges from six to nine months.
- **Trajectory calculations** and launch timing are critical for mission success.
- Understanding challenges like radiation exposure and gravity’s effects is essential for astronaut safety.
- Robotic pioneers set the stage for human exploration, gathering crucial data along the way.
- Future Mars tourism relies on technological advancements and rigorous safety measures.
FAQ
1. What is the average distance for a human trip to Mars?
The average distance from Earth to Mars varies greatly due to their elliptical orbits, ranging anywhere from about 54.6 million kilometers to over 401 million kilometers. Therefore, **time to reach Mars** depends on launch windows and the specific trajectory employed during **spacecraft navigation to Mars**.
2. How do future technologies impact Mars travel?
Innovations in propulsion systems and spacecraft design play a crucial role in shrinking the **Mars travel duration**. Technologies like electric propulsion and nuclear thermal engines are being researched to enhance speed and efficiency in interplanetary travel. These advancements will be essential for future **Mars exploration missions**.
3. What are the risks associated with Mars travel?
Risks include exposure to cosmic radiation, the psychological impact of isolation, and potential health complications due to lower gravity on Mars. Addressing these risks during human missions requires thorough training and treatment protocols to ensure astronaut safety throughout the entire **Mars journey duration**.
4. When is the best time to initiate a mission to Mars?
The optimal time for launching to Mars occurs during opposition, which happens approximately every 26 months. This timing allows for the shortest distance, reducing fuel costs and overall **Mars journey time**—essential for maximizing mission effectiveness.
5. Will there be opportunities for Mars tourism in the future?
Given the current trends in space exploration and technological advancements, there is potential for future **Mars tourism**. As private companies develop sustainable **Mars transport systems**, timelines and costs for tourists will become clearer, opening new frontiers in extraterrestrial travel.